tracing & communicating
the food supply chain
Cipriano Lopez
Katerina Philippou
Ricardo Punzo
Monique Chevalier

Slide 3
Slide 4
Slide 5-11
Slide 12
Slide 13-23
Slide 24-29
Slide 30-31
Project objective
Design methodology
Systemic Design approach
Check-in meeting (calibration)
Design Thinking approach
Solution proposal and strategies
End-consumer user experience (UX)
Index

Traceability
Accesibility
Our mission:
Improve traceability in the food supply chain by i) connecting the systems and the data of the different traceability systems and ii) offer useful information to customers to improve their sustainable behavior and to create an emotional bond with sustainably produced food products.
According to Deloitte there are four steps to help companies get ready for FDA’s Food traceability rule
1. Data Readyness
2. Process Readyness
3. Stakeholder Readyness
4. Technology Readyness
Data Governance
Data Foundation
Employee readyness
Process readyness
Supplier and consumer outreach and engagement
Technical Build
Project Objective
In order to understand the current situation and identify the real issues, we followed two methodologies:
1. Systemic Design
2. Design Thinking.
This process allowed us to immerse in the Agrifood supply chain
Systemic
Design
Design Thinking
Ideation
Problem
Solution
Diagnosis of territory
Best practice analysis
Problem identification
Solution development
Implementation
Methodology
Main takeaway: understand the complex ecosystem and interdependence of the food supply chain

- Policy: They guarantee a binding legal status with regard to European agri-food laws. There are many rules at European level, while at national level (Italy), the PNRR is the most important national investment for the development of the sector.
- Industry: Seeds and agrochemical suppliers, farmers, land owners, transformers, heavy machinery and equipment, food producers, retailers, big and small sellers, investors, IT providers and developers coexist and work to make the supply chain more efficient and competitive.
- Organisations: NGOs, local goverments, think tanks, startups, incubators, acelerators, research & development centres and universities are also key players.
- Users: End consumers, households, as well as businesses like hotels and restaurants. Based on their habits, it is possible to understand, which are the elements of the supply chain that work best and which do not.
Diagnosis of territory: Actors Map, Framing the system
Main takeaway: understand the key resources, how they have a correlation and connection with capabilities in the ecosystem

- Natural and Financial: The intricate food supply chain network is shaped by the fusion of natural resources and financial mechanisms. It is a dynamic and evolving ecosystem in which natural resources and financial capital converge to promote efficiency and sustainability.
- Human, Social, Cultural, Political: These elements intersect through knowledge, traditions, know-how and experience. This includes the technical and scientific knowledge that influences research and development associations and centres. The cultural aspect compensates for the high technicality and represents respect for traditions. The political area in which ideas, movements and forces are concentrated on several levels cannot be missing. The goals become concrete and are supported by laws at various levels.
- Digital: This area is developing into an increasingly complex reality with more information and data. Having the capabilities to manage this data is necessary to control this supply chain.
- Core: Transparency, traceability, and sustainability of the food system are complex areas that must be implemented as fundamental for safe, healthy, and sustainable food.
Diagnosis of territory: Multicapital Systems Map, understanding the system
Main takeaway: start to understand potential hypotheses and ways to make the food supply chain system more transparent, accessible, competitive and resilient.

- Transcending paradigms: These are critical areas often overlooked in building an efficient food supply chain. Neglecting these aspects not only destroys sustainability efforts, but also perpetuates social injustices within the global economic system.
- Paradigms: The implementation of a modern supply chain requires changes in mentality. Embracing these changes fosters resilience and promotes sustainable growth in the interconnected global market.
- Goals: Achieving these goals not only ensures sustainability, but also supports ethical standards and consumer confidence in the industry.
- Self – organisation: Strengthening the supply chain is possible through comprehensive training initiatives. In addition, providing incentives can further motivate engagement and drive continuous improvement.
- Rules and Regulations: Binding and more stringent laws are needed to ensure high quality standards
- Information flow: Improving transparency and access to crucial information is key to improving efficiency and resilience within the supply chain.
- Balancing and Reinforcing feedback loops: Through these activities we can improve stability and promote a positive escalation within the supply chain.
- Constants, Parameters, Numbers: These initiatives promote inclusiveness, environmental sustainability and ethical practices within the supply chain ecosystem.
- Delays: Critical delays within the supply chain system can cause significant damage and disruption in all industries.
- Structures: By focusing on these issues, we can optimise efficiency, resilience and transparency in the supply chain ecosystem.
- Buffering capacity: By prioritising these measures, companies can improve resilience, minimise disruptions, and contribute to environmental sustainability in their operations.
Diagnosis of territory: Intervention Strategy, exploring the possibility space
findings
Regulatory Variability - depending on type of food and location
Record where the product was sent (Forward) and where it came from (Backward) at each point in the supply chain.
Lack of recorded data
Lack of stickiness - simple user interaction
Consumer’s lack of Trust
Need for low-cost and effective technological solutions - intuitive
Verification of raw material sourcing
Relevance of data (timing), security and interoperability
The process of this research, underscores the complex interplay between compliance, transparency, and technology within the supply chain.
By dissecting these pain points we identified the foundation upon which the safety, integrity, and resilience of the entire food system is built.
These insights serve as a compass for future research, guiding efforts towards innovative practices that can enhance traceability, consumer confidence, and ensure that the agrifood supply chain operates effectively and ethically in a globalized economy.
Diagnosis of territory: Current systemic challenges, research
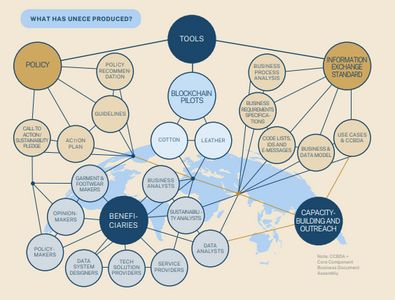
“FDA’s New Era of Smarter Food Safety blueprint aims for tech-enabled traceability, prioritizing digital tools for a safer and more digital, traceable food system to prevent and mitigate contamination.”
The Sustainability Pledge: Focused on the fashion supply chain


“Transparency and traceability underpin the Sustainability Pledge, offering tools like blockchain and DNA tracking solutions to authenticate sustainability claims in fashion. Joining the pledge allows companies to commit to more sustainable practices and inform better consumer choices.”

“The Traceability Playbook provides a step-by-step guide for organizations to build traceable supply chains, including methods for product identification, movement recording, and verification.”


The Institute of food technologist (IFT) and Global Food Traceability Center (GFTC) have created a toolkit to help better understand and conceptualize the design of traceability systems. These resources can also be used for a variety of cases including food safety, illegal/fraudulent products, and sustainability. The toolkit covers diverse food products (produce, dairy, seafood, etc).
Best practice analysis: Benchmark across industries
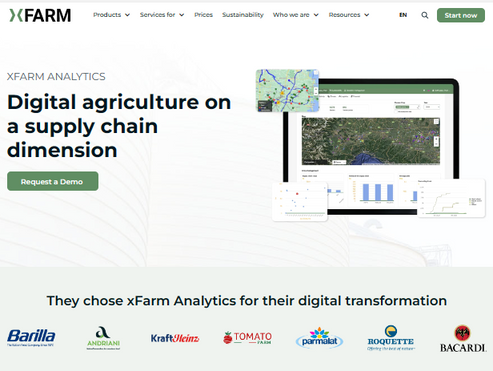
x farm is a technology platform designed to assist farmers and other stakeholders in the agriculture sector. It aids in digitizing various farming activities, including traceability in the supply chain of food products. The platform likely provides tools for monitoring and managing crops, analyzing data for improved decision-making, and facilitating the transparent movement of goods from farm to table

NutraSign is an app that leverages blockchain technology to provide farm-to-fork traceability, enabling businesses and consumers to identify and trace contaminated products within a food supply chain quickly. This user-friendly tool offers transparency for ethical concerns such as reducing carbon footprints and ensures that food operators and consumers can trace the entire food journey.
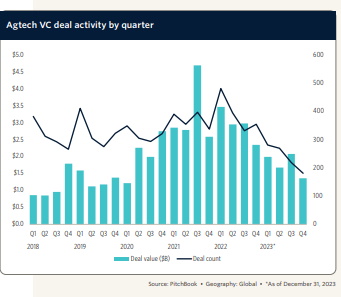
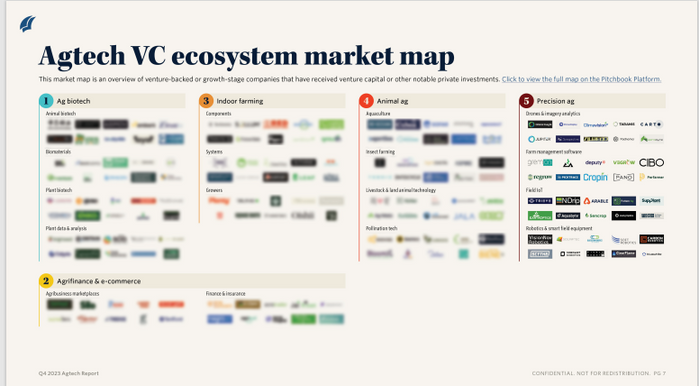
AGTECH ecosystem, has had significant growth and the increasing investment. A PitchBook report from Q1 2022 detailed that global AGTECH companies secured $3.3 billion across 222 deals, demonstrating high venture capital momentum driven by concerns for food security, advancements in data-driven productivity, and environmentally friendly agricultural techniques.



The Agrotech Conecta challenge, initiated by La Unión, a fruit and vegetable company from Almería, Spain, was won by a smart traceability solution for agroindustrial plants. This challenge is part of an open innovation initiative by the Andalucía Agrotech Digital Innovation Hub, aimed at connecting Andalusian agrifood companies with technological solutions offered by startups. The winners, D&A Innovative System, Datalsia, and Nutrasign, will collaborate with La Unión to develop and pilot this smart traceability system in a real-world setting

Best practice analysis: Benchmark in Agtech
Culture & behavior, Technology, innovation and new business models are needed to gain momentum
The Fintech ecosystem is very active and can complement global initiatives that are already in place.
The Agtech ecosystem, has had significant growth and continues to increase in investments.
The potential tools or solutions available in the market seem to be disaggregated and not interconnected. Most of the initiatives are working in silos.
The FDA has created the framework and guidelines to define a traceability food system. It has worked with the Institute of Food Technologists IFT (100 relevant actors) and Global food traceability Center to promote open innovation challenges to scout new startups working in the subject.
A global traceability initiative has been launched in the Textile Industry by de UN “Sustainability pledge” with very well structure framework, governance, and architecture. The question is why we don’t see it as consumers / users in the market?
Best practice analysis: Benchmarking research insights
Systemic
Design
Design Thinking
Ideation
Problem
Solution
Diagnosis of territory
Best practice analysis
Problem identification
Solution development
Implementation
check-in
Feedback and direction:
- The back-end exploration and benchmark was in a good track
- Explore ways to connect or integrate different applications and technologies
- Look for potential end to end solution
- The front-end has to be developed and work on the consumer engagement – Phygital and UX
Check-in: Meeting with the professors
Problem
Design Thinking
Ideation
Solution
Systemic
Design
Diagnosis of territory
Best practice analysis
Problem identification
Solution development
Implementation
Next steps:
- After using a systemic design approach, we leveraged the design thinking methodology to converge and identify the problem
- Deepening our recognition of the problem by identifying the main actors and their needs in the supply chain
- Understanding the key technologies we could use to bring about a solution
- Brainstorming, in order to find a solution that is valuable for all actors
- Proposing a physical user experience that allows the end consumer to engage and understand all the previous steps in the supply chain.
Problem identification: Convergence of Design Thinking Method
Grower / Producer
Transformer
Manufacturer
Retailer
End Consumer
Problem identification: Main players
Grower
Giulio Contadino
Chief Agricultural Officer
Oversees all agricultural activities within the farm

Directly involved in the cultivation or production of raw agricultural products.
Focused on sustainable practices and the quality of produce.
Has varying levels of technological sophistication and access.

Efficient ways to document and report on the origins, treatment, and handling of produce
Access to simple and affordable traceability technologies
Information on regulations and market demands for traceable goods.

High costs or complexity of implementing traceability systems.
Lack of knowledge or training on traceability tools and practices.
Variability in traceability requirements across markets
Transformer
Luca Trasformatore
Head of Processing Operations
Oversees transformation process of raw material goods into processed items

Processes raw agricultural goods into slightly altered forms (e.g., milling wheat into flour)
Positioned between producers and manufacturers, acting as an intermediary.
Quality and consistency of input materials are critical.

Reliable information on the source and quality of raw materials
Efficient systems for tracking inputs through the transformation process.
Ability to easily communicate traceability information upstream and downstream.

Coordinating traceability data across a network of suppliers.
Balancing the cost of traceability with the benefits
Ensuring the reliability and accuracy of traceability information
Manufacturer
Francesca Produttore
Director of Supply Chain Innovation
Her role is to integrate innovative tools for traching and tracing

Concerned with regulatory compliance, quality control, and efficiency
Uses a mix of local and global supply chains
Converts raw materials or slightly processed goods into finished products.

Detailed traceability data to ensure quality and compliance
Integration of traceability systems with internal manufacturing processes
Real-time tracking of materials for recall readiness and inventory management

Complexity of managing traceability across multiple ingredients and suppliers
High cost of advanced traceability technologies
Ensuring all suppliers meet traceability standards
Problem identification: Buyer Personas
Retailer
Marco Rivenditore
Quality Assurance and Compliance Manager, Enforces regulation and standards across all products

Sells finished products to end consumers
Focused on consumer trust, product authenticity, and safety
Often operates in a competitive market where differentiation is key

Reliable traceability information to assure consumers of product authenticity and safety
Systems that can manage and communicate traceability data efficiently
Ability to quickly identify and remove non-compliant or recalled products

Managing the volume of traceability data from various suppliers
Ensuring the accuracy of product information communicated to consumers
Cost and complexity of implementing consumer-facing traceability solutions
End Consumer
Sofia Consumatore
Mother
Concerned about the traceability of the products she consumes

Values transparency, safety, and ethical considerations in food products
Increasingly aware of and interested in the origins and journey of their food
Is often lazy and prefers simple actions when Going shopping

Accessible, understandableand reliable information about the food they consume
Assurance that food products are safe, ethically sourced, and of high quality
Ability to trace the product journey back to the origin without effort

Difficulty in accessing or understanding traceability information
Skepticism about the accuracy or honesty of traceability claims
Balancing desire for transparency with willingness to go out of the way to search for information
Insights
By capturing the perspectives of all players, we can design a solution that not only addresses the technical requirements of traceability but also aligns with the practical realities and constraints of each stakeholder.
Focusing on the commonalities and specificities in stakeholder needs, the solution can foster collaboration, compliance, and trust across the entire supply chain, ultimately leading to a system where traceability enhances value for all participants.
A key component is also to understand the role or job description of the personas across the chain in order to understand their skills and capabilities.
Problem identification: Buyer Personas
Digital passport (Already implemented for textile, batteries and electronics)
Accessibility & traceability
Digital identity
Cloud Storage
Physical
Digital
AR / Digital Twin
Blockchain
Smart Label
AI
RFID
Internet of Things
NFC
QR Codes
Through our analysis we identified an ecosystem where physical and digital technologies converge to provide a seamless framework for tracking and verifying the authenticity of products, services, and identities. The diagram shows key connections for potential integration points.
Conclusion
We must look into different platforms that are already applying these technologies in order to understand what is or is not working.
Ideation: Technology analysis
Understanding the variety and capabilities of these platforms is key to ideating the correct solution because it highlights the importance of interoperability, real-time data access, and the integration of different technologies for comprehensive supply chain visibility.
Therefore, this information will guide us to the development of a solution that can bridge gaps, enhance collaboration, and cater to the needs of the agrifood supply chain’s diverse stakeholders.
RFID tags, QR codes, and sensors
- Veemee
- Onfarm
- CropX
SCM Softare
- SAP
- Oracle SCM Cloud
- FoodLogiQ
- AgriDigital
The Cloud
- Atma.io
- Agrosmart
- FarmLogs
- XFarm
Blockchain
- Te-Food
- IBM Food Trust
- Vechain
- Provenance
- Traqfood
- ChainTraced
Ideation: Technology analysis, existing platforms

How can we connect different actors in the chain..?
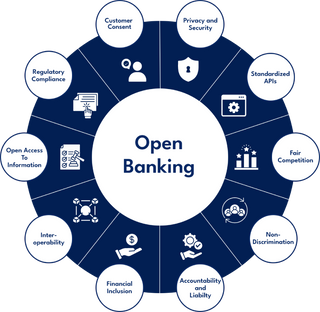
Driving inspiration from open banking and decentralized finance (De-Fi), envisioning an open-model platform for the agtech sector involves creating a unified system that seamlessly integrates various actors in the chain.
Just as open-banking relies on APIs to enable third-party developers to build apps and services around financial institutions.
Our idea was an open model that leverages APIs for data scraping and exchange among several traceability platforms. Similarly borrowing from De-Fi’s ethos, the platform would operate on decentralized networks to democratize access to information and reduce dependencies.
This brainstorming led us to draw parallels between the transformative potential of an open banking platform and the solution we are trying to provide.
Ideation: Brainstorming
Main Benefits of an open model
- Increased transparency: Ensures clear traceability throughout the chain, enhancing food safety and quality control
- Open Innovation: Open APIs enable the development of new applications, leading to continuous tech advancements and better agricultural practices
- Inclusivity: Democratizes data access, which provides opportunities to grow the industry
our
inspiration
Main opportunities of an open model
- Smart contracts in Supply Chain: Blockchain-based contracts can streamline operations, ensuring efficiency and trust among the chain
- Predictive analysis: AI for analyzing big data can lead to improving supply chain forecasting anf mitigating risks
- Sustainable Practices: sharing network of information on sustainable practices and their impact can incentivize and guide others to change their practices
We want to explore an open solution inspired in the DeFi - Decentralized Finance and Open Banking
Using API scraping, we could collect data from different players in the market and create a new data and information layer.
Ideation: Brainstorming, Why propose an open model?

our inspiration
Main Downsides of an open model
- Complexity & Integration challenges: Requires sophisticated technology that can be complex to integrate with existing systems
- Data privacy: Companies can share or expose their information if is mandatory or if there are the right incentives and trust among all players
- Dependency on current infrastructure: There is not a binding regulation for companies in the food value chain to share information like in the Banking industry
Conclusion
Is a good idea that could work, however at this point we don’t have the levers to push the initiative and we lack the technology know-how of the industry.
Therefore, we must continue our ideation process...
Ideation: Brainstorming, Why NOT propose an open model?

Moving on to the opposite side, our second brainstorm focused on what a closed model solution could look like.
Our inspiration was focused on different players in the food value chain and other industries like textiles and apparel are implementing applications that work well and could have a potential to scale and create more engagement with stakeholders.
Therefore, our solution is based on identifying the most complete and innovative platform already out there, in order to create a strategy to scale it.
Our closed model will be aimed at innovation, adaptability and transforming an existing solution.
How can we create a closed model solution..?
Ideation: Brainstorming - the opposite side, a closed model
Main Benefits of a closed model
- Controlled data management: Tighter control over data privacy and security, reducing risks of breaches
- Consistency: Stakeholders will know what to expect in terms of output and efficiency - which is crucial for planning and operations
- Streamlines support: A centralized system enables quick resolution of issues and updates, minimizing bugs and downtime

Through our research we identified that the best and most complete platform out there is atma.io
Main opportunities of a closed model
- Industry needs: Offers more customized and targeted solutions that address the unique challenges of the sector
- Strategic Partnerships: The development and scaling of such a tool can lead to strategic partnerships with key industry players (including the government) creating a more cohesive ecosystem in the agriculture sector
- Innovation within boundaries: Development of highly specialized solutions that meet the needs of agritech system without the complexities of an open ecosystem
Ideation: Brainstorming, Why propose scaling a closed model?
FAQs
Key features

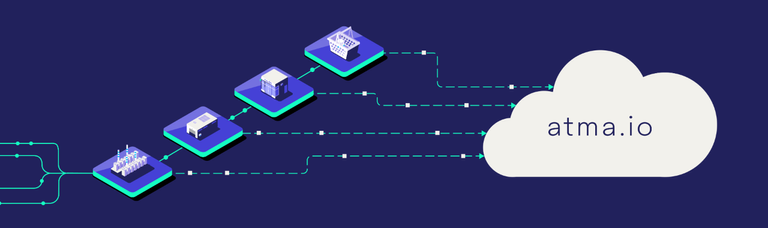
A digital platform that captures the full chain of custody along the supply chain and get real-time insights into the flow of products. Collects and shares information about where and how products are made and what they are made of.
atma.io enables tracking on a granular level which raw materials are used for production and capture the full genealogy of their products. As well as tracking, measuring, and analyzing the end-to-end carbon footprint for each product individually across the supply chain.




Traceability & transparency
Sustainability
& circularity
Consumer engagement
Powered by:


Key Technologies
Solution Development: Atma.io
Our proposal
Scale Atma.io by identifying a concise strategy in order to attract more players into the platform and therefore make it the main way to trace and track in the agrifood supply chain.
We will create a strong and appealing strategy that focuses on increasing the attractiveness of Atma.io

atma.io is a connected production platform powering a menu of third party front-end applications
The downside of this closed platform is that it could block the entrance of new market players, like other financial institutions different than MasterCard
Advantages of this tool
- "one-stop shop" that provides the label / digital trigger and software platform that create a connected product visibility
- Has the widest suite of use cases in the market, covering the true end-to-end journey from raw materials to the consumer and all the way back
- Product design philosophy makes the solution modular, and interoperable with any existing business infrastructure, giving flexibility for the business owners to use the platform that speaks to specific needs at the moment
How to acquire atma.io?
- Request a Demo: Interested parties to request a demo through their website (atma.io). This first step allows potential users to see the platform in action and understand how it can be tailored to their specific needs .
- Integration and Deployment: Atma.io works with businesses to integrate the platform into their existing systems. This includes assigning unique digital IDs to products and implementing the various modules required for traceability, sustainability tracking, and more at packaginginsights.com.
- Training and Support: Atma.io likely offers training for users and ongoing support to ensure successful deployment and maximization of the platform's benefits.
Price
Detailed pricing information is not publicly disclosed, since they offer customized pricing based on the scale of deployment, the specific modules used, and the level of integration required for each actor within the supply chain. Interested parties are encouraged to request a demo or contact Atma.io directly for pricing details.
Solution Development: Scale Atma.io
But first, we needed to understand
Why isn’t atma.io more diffused?
atma.io leverages various technologies such as QR codes, RFID, Bluetooth (IoT) and Cloud computing which offer several benefits like improved traceability, enhanced inventory management, and better customer engagement. However, there are a few gaps/ issues present within this platform...
Difficulty in fostering user engagement and retention could stem from a lack of gamification elements or integration with Mastercard services
Lack of User Engagement
Accessibility Concerns
The absence of an easy-entry strategy poses accessibility challenges, potentially excluding users with varying levels of technological proficiency.
B2B Focus
Potential challenge lies in transitioning from B2B to B2C market, requiring a shift in marketing strategies and user experience design
Solution Development: Scale Atma.io
Gamification
Leverage intrinsic motivation, and foster engagement through elements like rewards, competition, and progress tracking. Incorporating game-like features creates a sense of achievement and encourages continued participation.
Leaderboards:
Implement leaderboards to showcase top contributors or organizations based on their tracking and sustainability efforts. This can foster healthy competition and motivate users to actively participate in the platform.

Quests and Missions:
Design interactive quests or missions that guide users through different aspects of the supply chain process. For example, users could embark on a "sustainability quest" where they track and optimize the carbon footprint of a specific product from raw material sourcing to delivery.
Social Collaboration Features:
Integrate social features such as forums, discussion boards, or collaborative projects where users can share best practices, insights, and success stories related to sustainability and supply chain management. Encourage peer-to-peer learning and networking within the platform.
Solution Development: Strategy #1
Lack of user retention
Incentives
Leveraging Mastercard, one of the main partners of Atma.io, we can use their cashback rewards system for encouraging more players to join Atma.io
Some possible cashback programs could be...

Sustainability Rewards Program
(B2B)
- Earn a one-time $200 cash bonus for businesses that join atma.io and actively participate in providing transparent data about their supply chain activities within the first 3 months
- Earn unlimited 1.5% cash back on all transactions made through atma.io, encouraging businesses to conduct their supply chain activities via the platform

Transparency and Traceability Cashback Incentive
(B2B)
- Earn $200 cash back for businesses that join atma.io and provide comprehensive data about the origin of raw materials and the genealogy of their products within the first 6 months of account opening
- Enjoy 0% Intro APR (interest rate) on transactions made through atma.io for the first 15 months, encouraging businesses to adopt the platform for their supply chain activities. After that, a competitive variable APR will be applied based on creditworthiness

Conscious Consumer Reward
(B2C)
- Earn a one-time $200 cash bonus for consumers who sign up and make their first purchase of ethically sourced or sustainably produced products through atma.io within the first 3 months
- Enjoy unlimited 1.5% cash back on all purchases made through atma.io, encouraging consumers to support businesses that prioritize transparency and sustainability in their supply chain
Lack of user retention
Solution Development: Strategy #2
Easy access
We propose a few changes on the User Journey of the platform in order to increase the ease-of-entry of the users throughout the supply chain
Direct call to action
Reducing steps enhances the user experience by minimizing cognitive load, and improving completion rates allowing the user instant gratification through completing their subscription
Basic Subscription
Limited list of features for a specific type of actor in the supply chain
Premium Subscription
A more complete list of features for a specific type of actor in the supply chain
Fully Customized
A fully customizable list of features based on businesses wants and needs



Pricing models
These models are better for ease of entry because they offer simplicity and clarity to customers, making it easier for them to understand and choose the right option. Bundled pricing includes several features in a single package, eliminating the complexity of choosing individual components and ensuring transparency in pricing


A platform that unlocks the power of connected products providing unparalleled end-to-end transparency and tracking
Acquire today
Request a demo
Accesibility concerns
Solution Development: Strategy #3
When it comes to the end consumer...
Physical UX
Implement a Traffic Light System on food product labels to indicate the level of traceability and auditability in their supply chain
Green (Fully Traceable):
Demonstrates a high level of traceability and auditability throughout their supply chain.
Yellow (Partially Traceable):
Suggest that some aspects of their supply chain are traceable or audited, but there are gaps or limitations in transparency.
Red (Not Traceable):
Signifies that their supply chain lacks transparency and auditability.
Implementation:
- Regulatory Framework: Collaborate with government agencies and industry stakeholders to develop and implement regulations mandating the inclusion of the Traffic Light System on food product labels.
- Public Awareness Campaign: Launch a comprehensive public awareness campaign to educate consumers about the significance of the Traffic Light System and how to interpret the labels effectively.

B2B Focus
Solution Development: Strategy #4
When it comes to the end consumer...
Digital UX

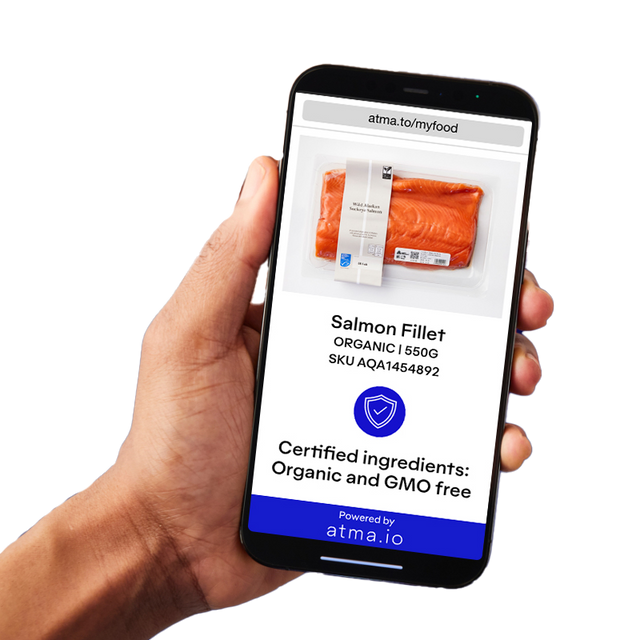
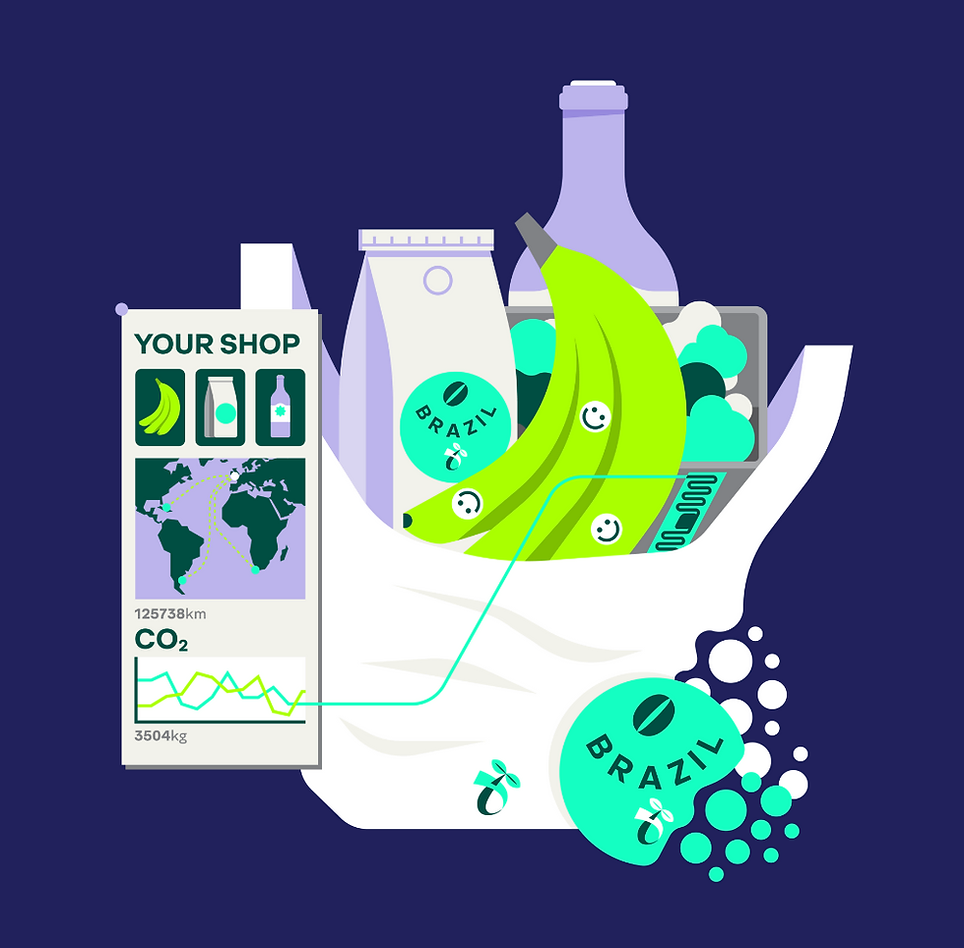
Atma.io engages with the end-user through their partner Smart Label, which has several digital features such as QR code scanning, nutritional value information of products, access to critical events along the supply chain and product recall information among others. We suggest enhancing those by implementing ...
Community Forums and Reviews:
A community platform within the app where users can share their experiences, ask questions, and leave reviews about products they've traced.
Personalized Recommendations:
Utilize machine learning algorithms to analyze consumer preferences and purchasing history to offer personalized product recommendations.
Augmented Reality (AR) Integration: Allows consumers to scan smart labels using their phone camera and instantly overlay information about the product's origin and ingredients directly onto the physical product packaging.
Integration with Third-Party Apps: Partnerships with other platforms related to health, wellness, and sustainability to integrate tracing capabilities seamlessly. For example, integrating with fitness apps to provide meal planning based on traced products.
B2B Focus
Solution Development: Strategy #5
Thank you
Cipriano Lopez
Katerina Philippou
Ricardo Punzo
Monique Chevalier